CHAPTERS
Navigate to chapter
► Chapter One: Flemish Giant Rabbit in Focus
► Chapter Two: Flemish Giant Requirements
► Chapter Three: Purchasing Your Flemish Giant Rabbit
► Chapter Four: Caring for Your Flemish Giant Rabbit
► Chapter Five: Meeting Your Rabbit’s Nutritional Needs
► Chapter Six: Breeding Your Flemish Giant Rabbit
► Chapter Seven: Grooming Your Flemish Giant Rabbit
► Chapter Eight: Showing Flemish Giant Rabbits
► Chapter Nine: Keeping Your Rabbit Healthy
Chapter One: Flemish Giant Rabbit in Focus
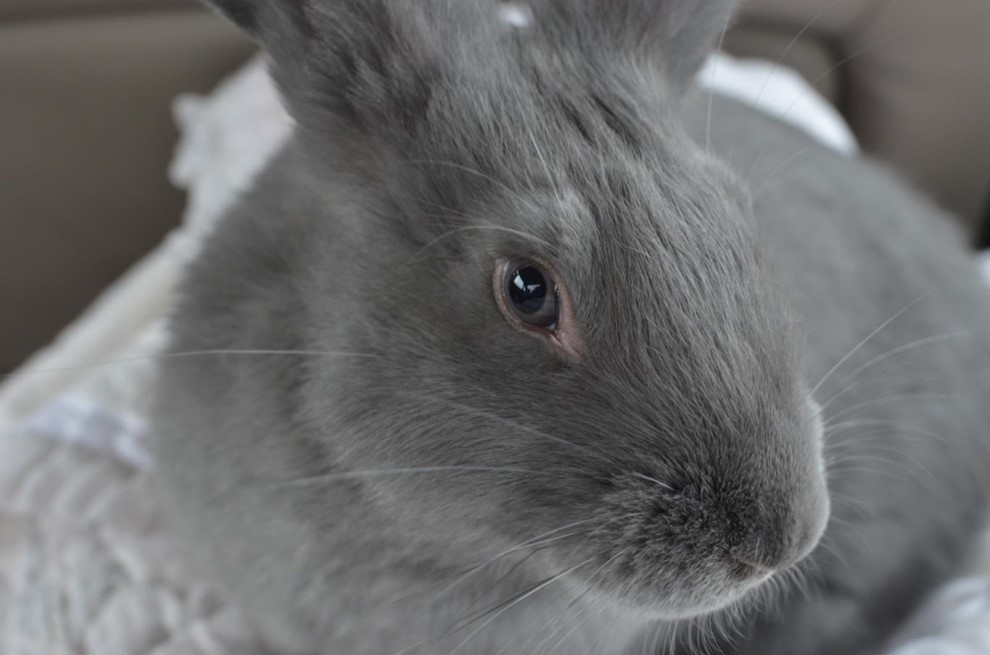

Flemish Giant rabbits may often time look like your protective brother, your supportive parents, your calm pal, your playful sibling or that very adorable kid you always wanted. In whatever attitude or mood it appeals, you can expect it to be docile yet interactive and a caring devoted pet you’ve always dreamed of.
The Flemish Giant rabbit is a breed of rabbit that is eligible for shows. They are irresistibly cute but it may not be the right choice for everyone. Before you decide whether or not it might be the right pet for you and your family, you need to learn and invest a significant amount of time in getting to know these animals.
In this chapter you will receive an introduction to the Flemish Giant rabbit breed including some basic facts and information as well as the history of how it came about. This information, in combination with the practical information about keeping Flemish Giant rabbit in the next chapter, will help you decide if this is the perfect rabbit companion for you.
Facts about Flemish Giant Rabbits
In this section you’ll find some interesting fun facts about Flemish Giant rabbits, how to differentiate them through their body type, the types of their mane and history.
Flemish Giant rabbits are large sized rabbits that have a large semi-arch type body and a broad head with erect ears. They like to be around people and have a knack for a good time but don’t let their cuteness fool you, like any rabbits, they can get scared and be wary especially around strangers, and if it feels threatened it may cause aggression, which is why it is advisable that owners should socialize them at an early age.
Male Flemish Giant rabbits have broader heads than females. The females have dewlap or a large flap of skin under their chins to protect and keep their baby bunnies warm. There are seven official colors for the Flemish Giant breed these are Black, Blue, Fawn, Light Gray, Steel Gray, Sandy, and White.
Even if Flemish Giant rabbits are a fairly new breed, they are now qualified for a rabbit show and it is recognized by the British Rabbit Council (BRC), American Rabbit Breeders Association (ARBA), United States Flemish Giant Rabbit Club as well as international rabbit organizations like the European Confederation of Rabbits, Pigeons and Poultry.
The Flemish Giant rabbit is a very docile, intelligent, friendly creature and a highly trainable breed, this breed also have wide variety of colors and patterns created by breeders and rabbit enthusiasts although only seven are officially recognized. Flemish Giant rabbits are also fond of chewing like any other pets, and they can comprehend certain orders as well. They can even respond to their name which makes them great house pets much like cats and dogs; the only difference is that these rabbits can be high maintenance. They cherish people with whom they form very strong bonds with. They are gentle and understanding and they can are naturally people-oriented.
Proper socialization and training from a young age will help prevent the rabbit from being aggressive to people. Flemish Giants do very well as family pets and they can also be good with children – although may not be recommended for very young children.
The Flemish Giant has a long and powerful body type; they are one of the largest rabbit breed in the world. This breed weighs an average of 14 pounds; the heaviest recorded Flemish Giant reached 21 pounds. They also have bold and bright eyes.
Like any other pets, rabbits also have a great deal of energy and needs daily exercise to work off that energy through the toys that you can provide. It can adapt to almost any kind of environment, they are generally curious yet controllable indoors as long as they get enough mental and physical stimulation during the day and has proper house training as well as litter training.
The average lifespan for the Flemish Giant breed is between 8 and 10 years, longer than the average rabbit breed; the breed is very healthy in general. Like many rabbits, however, the Flemish Giant is prone to health issues such as Calcivirus, Pasteurellosis, Pneumonia, E. Cuniculi, Ringworm, Hepatic and Intestinal Coccidiosis, Abscesses and Urine Burn which will be tackled in the next few chapters later on in this book.
In terms of grooming, the Flemish Giant rabbits have short coats that need to be brushed and groomed at least once a week to keep their coat and skin healthy, a daily brushing may be required for some especially when they are molting.
This section will give you an idea on what kind of body type your Flemish Giant rabbit may have and how you can distinguish it from other kinds of breed. Aside from the ear type, you can also differentiate a rabbit through the type of its fur.
Here are the general body types and shapes of rabbit breeds according to the ARBA:
Full Arch
These rabbits have an arched back that starts at the nape of the neck, arching to the tail.
Semi-Arch (or Mandolin)
Flemish Giant rabbits are classified under this body type; they have an arched back that starts behind the shoulders and arches to the tail. They have a well-defined rise of arch near the shoulders; the highest point of the rise occurs at the top of the hips.
Compact
These rabbits are lighter and shorter in length than meat rabbits, usually kept for show or kept as pets.
Cylindrical
These rabbits have a long, thin, rounded body with small bones and a long, slender head.
Commercial
These are rabbits that are medium in size with bodies about as wide as they are deep.
You can also differentiate a rabbit through their purpose or the reason why they are bred in the first place. It can be shown by the type of their fur or body shape.
Meat Rabbits
These rabbits grow quickly and are usually ready for slaughter by about 8 to 12 weeks of age. Originally, Flemish Giants are bred for its meat.
Fur Rabbits
These rabbits are bred for their soft, thick fur which can be used for coats and trim on clothing. Flemish Giants can also be under this category.
Wool Rabbits
These are rabbits which produce wool in the same way that a sheep produces wool.
Continue Reading…
Want to read the entire thing?