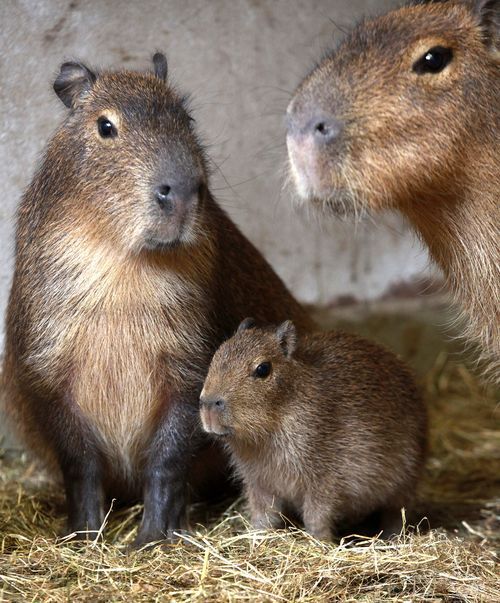
Capybaras can reach up to 1.4 meters long and weighs around 75kg; which about the same size of a large dog breed; making them the largest rodent in the world. Despite their gigantic size however; they’re quite good swimmers. They have adapted well to aquatic lifestyle; and they live close to fresh water sources to escape from land predators.
Their barrel-shaped body makes them look heavy, while their short head and muzzle make them easy to distinguish as rodents. Their eyes, nose and ears are all strategically positioned on top of their head; allowing them to see, breath and hear effectively while their bodies are submerged underwater. They’re pretty excellent swimmers as well, thanks to their webbed-feet similar to ducks.
Behavior and Lifestyle
Capybaras are highly sociable animals. They tend to live in groups which are comprised of 10 to 20 individuals. They can also merge with other herds and make one large herd. Their herd is ruled by a dominant male with females and their young. A herd of capybara usually occupies stable ranges of home that vary in size; depending on the needs of the herd of course. They choose their environment wisely, and they make sure there are plenty of foods. They may overlap with another herd sometimes, and they usually chase intruders.
These animals don’t sleep much, rather; they wallow in the water or mud to cool down during hot days, or rest in the thickets in river banks in the morning. They graze on grass and aquatic plants in the early evening and continue throughout the night.
Reproduction and Life Cycles
As with most mammals living in herds; it is only the dominant male that has the right to breed with the females in their herd. Their breeding season can occur throughout the year, depending on many factors. Breeding season for capybaras is usually during rainy season, which is around April and May. They become sexually mature around 18 months, and breeding takes place in the water.
After a few months of gestation (around 5 months or 150 days); female capybaras will give birth to one to eight young pups on land. The newborn will weigh around 2 to 3 lbs., and well-developed; they can see, and already completely covered with in hair. They can walk, or even walk after a few hours of birth; and can run and swim after just a few days of birth.
The female capybara then rejoins the main group after a few hours, along with the newborn. The baby capybaras are able to eat grass after only a week; but they will continue to get their milk from their mother until they’re around four months old. What is even more interesting about female capybaras is that; all the females in the herd share the responsibility to milk the young capybaras, as well as provide care and protection.
In the wild, capybaras can live up to 10 years; or 5 to 8 years on average, and a little longer in captivity, which is about 12 years.





 Author and long-time animal lover. Sharing knowledge on pet care through experience and the written word.
Author and long-time animal lover. Sharing knowledge on pet care through experience and the written word.