Table of Contents
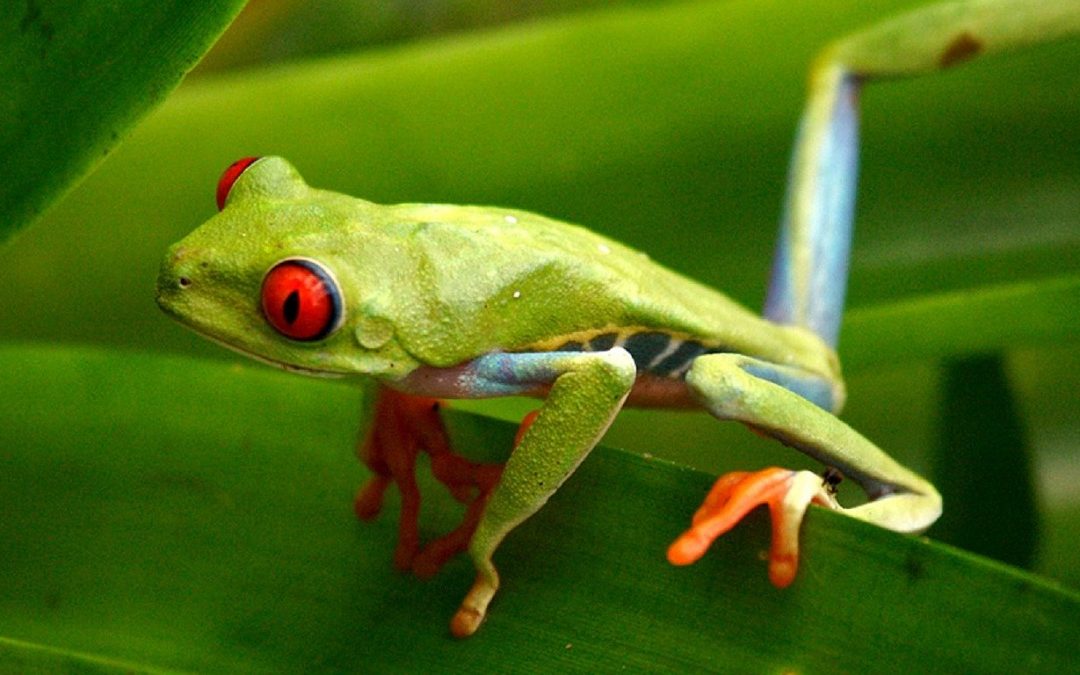
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Red-eyed treefrogs can be found throughout many of Central America and also as much north as southerly Mexico. What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Red-eyed tree frogs live in tropical jungle areas, where they are typically found in the lowland rainforests as well as bordering hillsides, particularly in areas near to rivers or ponds. What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? They prefer temperatures between 75-85 levels Fahrenheit during the day, in between 66-77 degrees Fahrenheit throughout the nighttime, and humidity at around 80%-100%.
Suction – Cup Toes
Red-eyed tree frogs are outstanding mountain climbers and have suction-cup toes that assist them attach themselves to the underside of fallen leaves, where they rest throughout the day. They can likewise be located holding on to branches as well as tree trunks throughout their habitat and also are qualified swimmers if essential.
Carnivorous Frogs
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Red-eyed tree frogs are carnivores that feed mainly in the evening. The red-eyed treefrog’s eco-friendly coloring permits it to remain concealed amongst the leaves of trees, waiting for pests or other tiny invertebrates ahead their way. Red-eyed treefrogs eat any kind of animal that fits right into their mouth, but their typical diet regimen is composed of crickets, moths, flies, insects, as well as in some cases even smaller sized frogs.
Red – Eyed Tree Frog Adaptions
Red-eyed tree frogs are known leading for their massive, brilliant red eyes, a feasible adjustment to nighttime activity or the main part of a defensive approach called startle coloration. Red-eyed treefrogs have huge, specifically established suction mug toe pads, which permit them to connect to leaves, branches, and also the sides of trees
Males vs. Females
Female red-eyed treefrogs are usually larger than the men with a grown-up size of as high as 3 inches. Male red-eyed treefrogs typically get to an adult size of regarding 2 inches.
Red – Eyed Tree Frog Reproduction
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Red-eyed tree frogs typically duplicate in the wet season. A croaking and shuddering mating routine launches reproduction. Red-eyed treefrogs utilize a procedure called amplexus, an usual kind of recreation for frog species. During amplexus the smaller sized male holds the larger lady and also feeds the eggs as they arise from the female. The male does not allow go of the woman until the eggs have actually been laid, which might continue for a day or longer.
Clutch
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? As recreation occurs on the bottom of leaves, the female must hold on to the fallen leave with her suction-cup toes, hanging on for both herself and her companion. After each clutch of eggs that a women generates she needs to enter the water with the man still affixed to her back, in order to load her bladder with water. Her eggs will dry out up as well as pass away if the female does not fill her bladder between clutches.
Egg Process
When the clutches of eggs have actually established right into tadpoles, which occur swiftly, the tadpoles swim around within their eggs until the egg tears. The fracturing of all the eggs in the clutch happens within a one min time period, and also the fluid released from the fractured eggs aids to clean all the tadpoles down the fallen leave and also into the water below.
Behavior of Red – Eyed Tree Frogs
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Red-eyed tree frogs are nocturnal as well as rest throughout the day. If a predator were to occur upon a red-eyed treefrog, the frog would certainly awaken, as well as its eyes would unexpectedly pop open.
Music Breeding
The music breeding ritual of red-eyed treefrogs starts with the loud croaking of one red-eyed treefrog that is promptly joined by the various other male red-eyed treefrogs in the location with all sharing the common goal of bring in females. This loud croaking continues as male red-eyed treefrogs leap from one leaf to one more in a frenzied effort to establish territory. Male red-eyed treefrogs are likewise understood to “quiver” to attract women.
Quavering
What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Quavering takes place when the loud croaking is at its orgasm. Male red-eyed treefrogs inflate their vocal cavities and rise on all fours in an attempt to bring in women as well as discourage other men from entering their area. Throughout this procedure, at the very least 2 males deal with each other and also quiver, their bodies violently trembling. This shuddering routine establishes territory as well as demonstrates strength and scare tactics.
Mating Rituals
During this process, when sparked by even the tiniest movement, male red-eyed treefrogs duke it out other men, and often many males climb on top of each other. At some factor throughout this mating ritual, trying not to draw in too much attention, the ladies gradually come down from the treetops. As soon as the females have actually been observed, several males will get on her back, combating each various other for the ideal positioning. The best-positioned man is the one that is right on her back and can secure his limbs around her stomach. Often numerous men will certainly remain on her back for days up until she locates an appropriate spot to lay her eggs. All the men try to feed her eggs when she is in this spot.
Conservation Status
These frogs are ruled out threatened in their native environment. Nonetheless, there has been much problem regarding the general problem of the rainforest in which red-eyed treefrogs live. What you need to know about red – eyed tree frog? Worldwide warming, logging, weather and also climatic changes, marsh water drainage, and also contamination have triggered remarkable declines in the amphibian populations of the jungles of Central and also South America.





 Author and long-time animal lover. Sharing knowledge on pet care through experience and the written word.
Author and long-time animal lover. Sharing knowledge on pet care through experience and the written word.